Embedded Finance – The Game Changer of Fintech
The emergence of fintech has revolutionized the way people earn, save, and spend. Valued at around $194 bn in 2022, the global fintech sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.8% to reach $492 bn by 2028.
Today, businesses across industries are evolving with fintech as the catalyst. They use fintech as a competitive advantage to drive differentiation and profitability. Fintech startups are growing as investments pour in despite macroeconomic resets and regulatory headwinds. Banks, NBFCs, and other businesses are keenly eyeing fintech collaborations to stay ahead of the curve.
Embedded Finance is the key driver that enables fintech collaboration by seamlessly weaving in financial services/products into any non-financial customer experience, journey, or platform. Expected to witness 5X growth by 2025 with the market size valued over $250 billion, it could be the flagbearer for the next revolution in digital payments.
What is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance refers to the contextual integration of financial services into diverse non-financial services. Practical examples include cases where contactless checkouts, Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL), and other consumer lending options are added onto a retailer/ecommerce merchant application. Or travel insurance, card payments, and UPI payment facility available in cab hailing apps. The technology redefines and reengineers the distribution channels for financial services such as payments, insurance, lending, and other emerging segments.
The global embedded finance market was valued at $54.3 bn in 2022 and is expected to grow at 16.4% to reach $248.4 bn in 2032. The rise in cloud computing and open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) has played a great role in making embedded finance accessible to everyone. Changing consumer behavior, preference for digital over brick & mortar, and success of early adopters such as e–commerce players/retailers and non-traditional FIs are paving the way for greater adoption and growth of embedded finance. Today, several embedded financial solutions are built around payment gateways, insurance, cloud banking, compliance, personal finance, and more.
Growth Drivers
The rise of new-age customers, the sharing economy, Peer to Peer (P2P) transactions, and mobile commerce serve as key accelerators to embedded finance. The pandemic provided a significant impetus as it triggered a massive shift in customer preference towards personalized, secure cashless transactions, thereby increasing the use cases. It catalyzed digitization across sectors and drove the dramatic increase in online platforms to deliver quick, convenient, and personalized financial services.
Key Ecosystem Players
There are three key players involved in the embedded finance ecosystem.
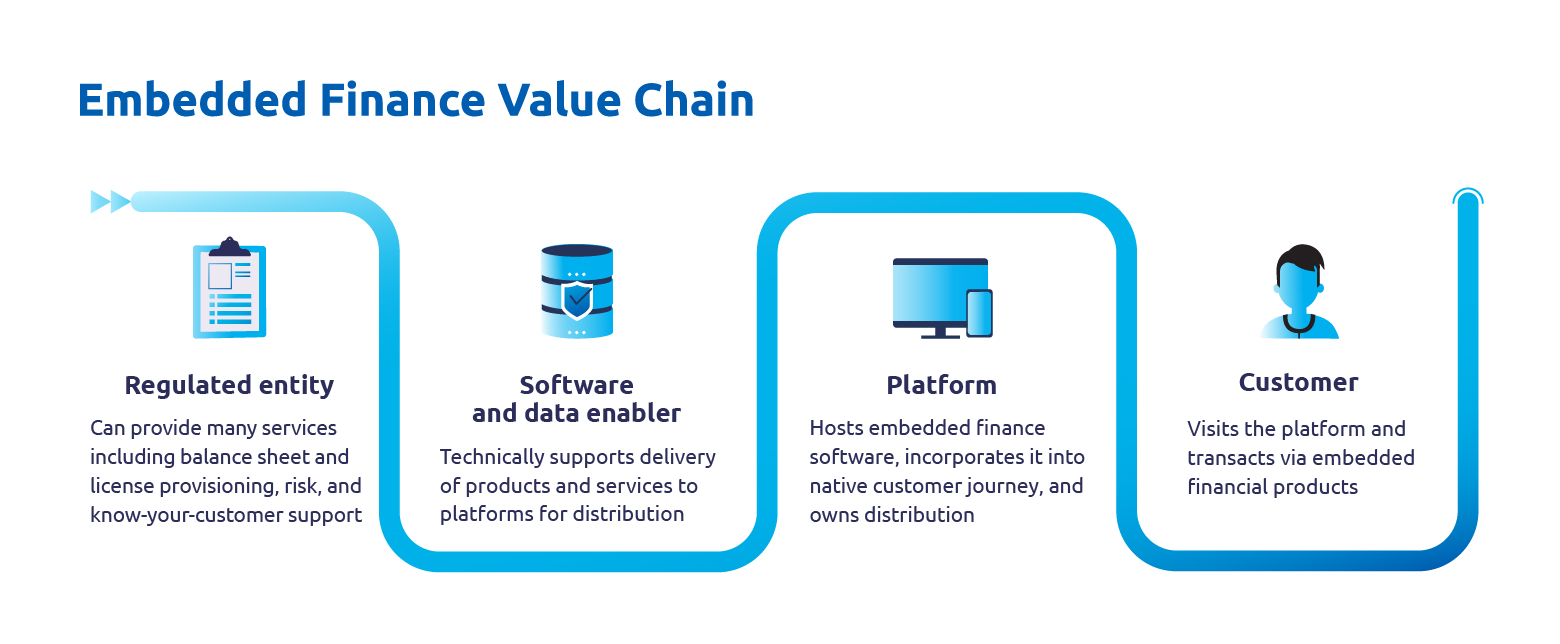
- Financial Institutions: Banks and NBFCs leverage their network, risk management capabilities, and customer goodwill to facilitate embedded financial services and infrastructure.
- Solution & Platform Providers: Businesses with customer-facing platforms such as mobile apps and websites (that require financial integrations) work with solution providers (in this case Fintechs) to embed payments, insurance and lending services.
- Data Enablers: Data aggregators and managers that transport data back and forth between the solution providers and digital platforms are critical players in embedded finance.
Types of Embedded Finance Applications
Every business is different and has unique needs. Embedded finance manifests itself in versatile ways to cater to customized requirements.
- Embedded Payments: Digital payment options that are implanted into the checkout pages of applications and platforms are called embedded payments. Integrating these makes it easier for customers to pay for goods and services within the application. Examples: Ecommerce checkout pages like Amazon with multiple payout options.
- Embedded Investments: Seamless integration of investment and advisory services into non-financial application is what embedded investments offer. Investing becomes a simple process as customers get the convenience of managing their finances and obtaining market information and analysis from a single place. API-based brokerage firms have popularized this trend by creating APIs for various microservices, such as account creation, funding, trading, portfolio management, investing. Example: Social media companies like WeChat that offer wealth management, investment and advisory services.
- Embedded Lending: Providing customers instant access to digital credit, embedded lending offers loans via non-financial platforms. It eliminates the need for expensive third-party intervention, lengthy paperwork, and tedious processes. Example: HR tech platforms like Payactiv that processes employee loans, and food delivery apps like Swiggy that provides BNPL credit.
- Embedded Insurance: Removing all the complexities involved in getting an insurance service, embedded insurance simplifies the bundling and sale of insurance coverage or protection during any purchase. It delivers effortless coverage to consumers in real time by integrating transactional APIs and technologies with mobile apps, websites, and other partner ecosystems. Example: Travel booking apps like Cleartrip that offer flight insurance.
- Embedded Donations: Donating to a cause right after a transaction is a new way of charity made easy by embedded finance. Also called “embedded giving”, this charitable act makes it simple for people to give to charity and encourages them to give to a wide range of causes. Example: Lifestyle stores ask their customers to add a small amount to their bills to help local causes like food banks and child support.
Now this is not all. Embedded finance can also branch out as embedded banking, embedded wealth management, and more.
Opportunities in the Embedded Finance Market
The goal of embedded finance is to make it easier for customers to manage their finances and eliminate the need to switch providers. With a lot of growth expected in this market, businesses that use embedded finance have many opportunities:
- By adding technology to traditional financial services, businesses can offer a wider range of products and services.
- Growing a business in collaboration with an embedded partner is more successful than doing it alone.
- After the rise of professional investors, embedded finance fostered the growth of specialized business models like platform companies and the establishment of big fintech funds, business incubators, and accelerators.
- Embedded funding and financing will evolve with time to help businesses raise capital and gain greater market share.
Benefits of Embedded Finance
Boosts revenue
- A viable way for businesses to increase revenue without increasing the price of their product.
- Enables cost-efficient customer acquisition and retention.
Eases customer process
- Fosters customer convenience by facilitating branch-agnostic banking and insurance services to customers across demographics.
- Fulfills the desires of the new-age customers to make payments conveniently and quickly without using physical cash.
Supports Banks
- Improves customer retention by enabling banks to use customer data to personalize services and attract/retain customers.
- It’s a great way for financial institutions to expand their customer base and keep them coming back for more.
Increases Brand Image
- Embedded financial solutions improve customer experience thereby boosting brand image.
- By driving the next generation of innovative and transformative financial products, it will serve as the foundation for brand development.
Aids Fintech advancement
- To create an amazing customer experience, the financial platform of the future is built by combining cutting-edge technology, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Financial Industry + SaaS = Greater Value. Consumers will have access to more advanced financial services within the main application, offering a higher level of value.
Embedded Finance Use Cases
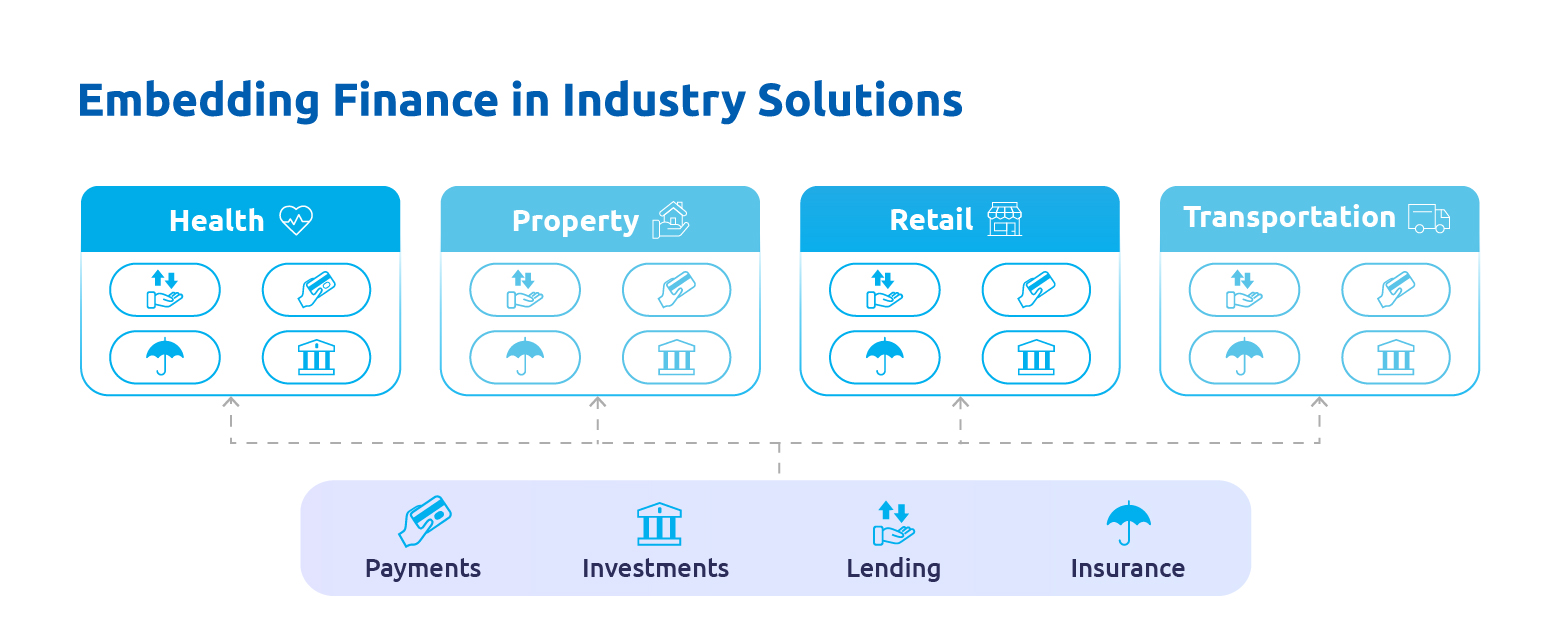
Being an integral part of fintech, embedded finance includes everything from mobile banking and peer-to-peer lending to digital currencies like CBDC. It is a great way to grow your business without the need for large capital investment. From cryptocurrency ATMs to a company that offers an insurance product based on the volatility of Bitcoin, embedded finance is becoming the new normal. The use cases span across industries such as healthcare, automotive, education, agriculture, and real estate, apart from ecommerce, retail, financial services etc.
BNPL: Buy Now Pay Later is an important embedded credit use case. It allows consumers to purchase goods and services upfront and pay for them in installments over time. Many retail and ecommerce businesses have embedded BNPL onto their checkout pages to offer flexible payments that increase sales and improve customer loyalty.
Cashless Transactions: Embedded finance enables customers to make cashless payments seamlessly within a mobile app or website, without the need to navigate to a separate payment gateway or bank transfer. This is done by integrating mobile wallets to mobile applications or e-commerce platforms. With a few clicks on their smartphone or tablet, users can link their credit or debit cards to their mobile wallet or scan QR codes to make payments.
Insurance: Insurance providers can offer customers loans or investment opportunities to help them finance the premiums for their policies or invest their funds for better returns. These embedded finance applications reduce the cost associated with silos and intermediaries. Insurance and financial processes are streamlined by leveraging data analytics and automation which improves customer engagement and loyalty.
Lending: Embedded lending comprises full stack lending solutions that encompass KYC, onboarding, underwriting, customer experience support and bank partnership management. These integrations help lenders focus on their core operations, customer acquisition and market expansion, while embedded credit providers manage the technology heavy lifting. Embedded finance also empowers lenders to be more inclusive and offer loans and credit products to a broader spectrum of individuals and enterprises.
Challenges through the way
Just as there are two sides to a coin, embedded finance comes with a few challenges. Here are a few of them.
- Overcome traditional banks’ resistance to change, as well as the need for improved collaboration between fintech and legacy institutions.
- Regulatory compliance with the integration of financial services and products into non-financial products must be audited on a regular basis.
- Data protection and privacy to comply with appropriate regulatory frameworks.
- Hiring the right people to maintain the high rate of innovation in practical applications.
Now, it is important to note that the barriers listed above can be removed skillfully if there is a keen focus on compliance, risk management, and building a culture of innovation and security. Using AIL and ML based tools will help clear the roadblocks.
Road Ahead
Embedded finance is the future of fintech. Its context-led, hyper-personalization capabilities and data-driven business processes will serve as a key differentiator for businesses of various sizes and scales. It can take your business to the next level by adding value to customers, generating revenue, and lowering costs. With emerging technologies, such as AI and blockchain, financial institutions can develop novel financial products and services along with improving customer experience. The ability to evolve with newer business models and adapt to regulatory and legal changes are critical for businesses to thrive in the domain.
If you find this blog to be useful, please forward it to fintech enthusiasts and entrepreneurs you know.
Join our Tether Community Forum and stay updated with the ongoing trends in Fintech. Be a part of India’s thriving financial technology revolution by signing up for the #TetherCommunity today!
There’s more information coming your way with our next blogs. Keep reading!


